
判断 Pod 健康状态的两种方式
- livenessProbe 存活性探针
- readinessProbe 就绪性探针
1.livenessProbe 存活性探针
用于判断容器是否存活,即 Running 状态。如果 livenessProbe 探针检测到容器不健康,则 kubelet 会杀死容器,并根据容器的重启策略进行容器的重启。如果容器没有定义 livenessProbe 探针,则 livenessProbe 返回状态永远为 Success。
2.readinessProbe 就绪性探针
用于判断容器服务(service)是否可用,即 Ready 状态。如果 Ready 状态,则表示Service 与 Pod EndPoint 建立了关联,并且将其保存到 EndPoint 列表中,以供服务调用;如果状态变为 Failure , Kubernetes 会将其从 EndPoint 列表中移除,保证通过 Service 访问时不会将流量路由到不健康的 Pod 上,等到状态恢复到 Ready 状态再将其对应的 EndPoint 加入EndPoint 列表中。如果容器没有定义 readinessProbe 探针,则 readiness 返回状态永远为 Success。
探针的配置方式
通过 kubectl 定期对容器进行诊断,判断容器状态是否健康或者存活。
livenessProbe 和 readinessProbe 探测方式
- ExecAction
- TCPSocketAction
- HTTPGetAction
三种探针的可能返回结果
- Success:探测成功
- Failure:探测失败,更具重启策略重启容器
- Unknow:探测失败(未找到),不采取任何行动

ExecAction
在容器中执行自定义命令以判断容器是否健康,命令退出时返回码为 0 ,则表示健康,其他值表示不健康。
例子:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
test: liveness
name: liveness-exec
spec:
containers:
- name: liveness
image: innerpeacez/k8s.gcr.io-busybox
args:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- touch /tmp/healthy; sleep 20; rm -rf /tmp/healthy; sleep 60
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- cat
- /tmp/healthy
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 5
这个例子中,busybox 镜像其中之后执行了 touch /tmp/healthy 创建出 /tmp/healthy 目录,30 s 后删除这个目录,livenessProbe 设置了 initialDelaySeconds: 10,会在容器启动之后 10s 后进行初次探测,返回结果不出意外为 Success ,表示容器健康。使用以下命令查看 Pod Event
kubectl describe pod liveness-exec
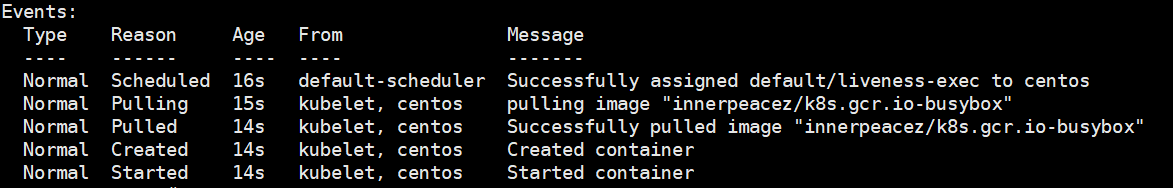
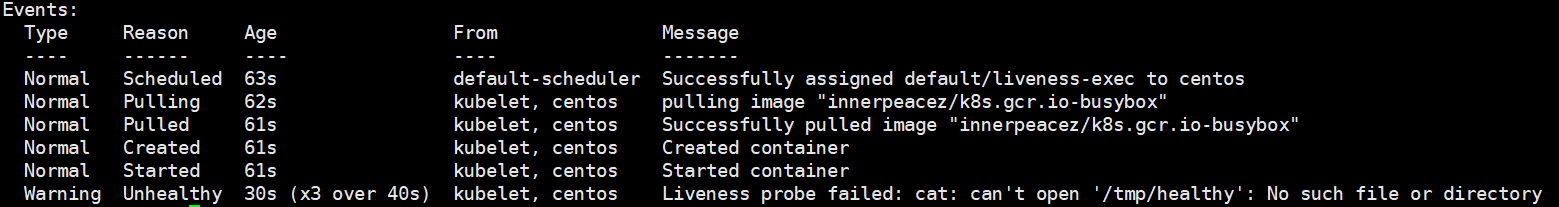
一段时间后你可能会看到以下结果,显示目录不存在了。原因是periodSeconds: 5设置了 5s 后再次探测,但是目录已经被删除了,所以探测返回结果为:Failure。
TCPSocketAction
通过容器的 IP 和 port 进行 TCP 检查,如果能够建立 TCP 连接,则表示容器健康。
例子:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: liveness-tcpsocket
labels:
app: liveness-tcpsocket
spec:
containers:
- name: liveness-tcpsocket
image: innerpeacez/k8s.gcr.io-goproxy:0.1
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
livenessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 15
periodSeconds: 20
执行命令:
vim livenessProbe-tcpSocket.yaml # 将上面内容粘贴进来
kubectl apply -f livenessProbe-tcpSocket.yaml
例子中,livenessProbe 会与容器中的 localhost:8080 建立 TCP 连接,进行健康检查。因为容器启动时,容器端口被设定为 8080,所以可以建立 TCP 连接,livenessProbe 健康检查返回 Success 。我们可以手动将 tcpSocket 检查端口设置为 8081 ,此时将无法建立 TCP 连接,可以通过下面的命令查看 Pod Event。
kubectl describe pod liveness-tcpsocket
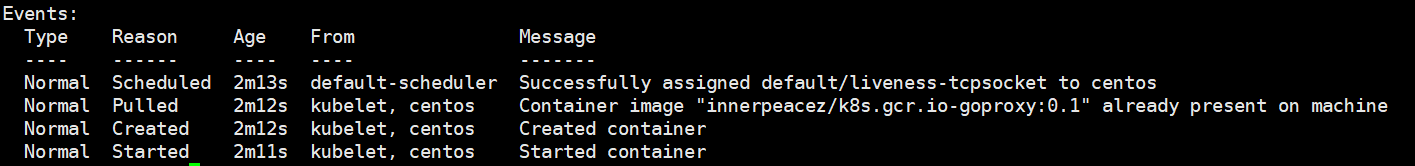
修改成 8081 再次查看 Pod Event
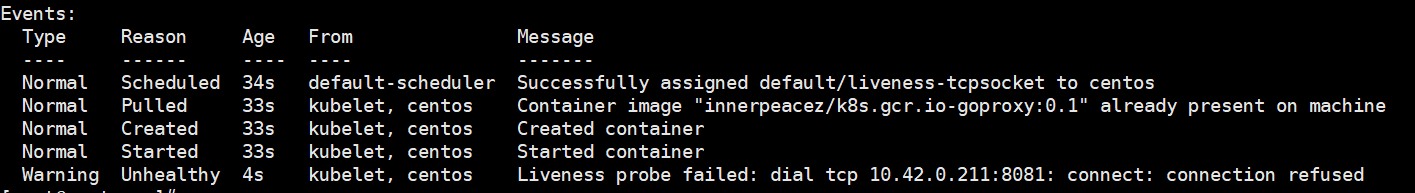
可以看出 unhealthy ,证明 tcpsocket 检查返回值为 failure 。
HTTPGetAction
通过容器的 IP Port 以及访问路径,发送 HTTP 请求进行调用,如果返回的状态码范围为 [200 , 400) ,则表示容易健康。
例子:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
test: liveness
name: liveness-http
spec:
containers:
- name: liveness
image: innerpeacez/k8s.gcr.io-liveness
args:
- /server
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 8080
httpHeaders:
- name: Custom-Header
value: Awesome
initialDelaySeconds: 3
periodSeconds: 3
执行命令:
vim livenessProbe-httpget.yaml # 将上面内容粘贴进来
kubectl apply -f livenessProbe-httpget.yaml
同时可以执行以下命令查看 Event
kubectl describe pod liveness-http
readinessProbe 探测
方式和 livenessProbe 是一样的,所以上述设置 livenessProbe 的地方同时也可以设置 readinessProbe 。如:
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- cat
- /tmp/healthy
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 5
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- cat
- /tmp/healthy
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 5
livenessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 15
periodSeconds: 20
readinessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 15
periodSeconds: 20
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 8080
httpHeaders:
- name: Custom-Header
value: Awesome
initialDelaySeconds: 3
periodSeconds: 3
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 8080
httpHeaders:
- name: Custom-Header
value: Awesome
initialDelaySeconds: 3
periodSeconds: 3
livenessProbe 和 readinessProbe 相关配置
如上述的 initialDelaySeconds ,表示初次进行探测的时间,以下是完整的配置列表
| configure probe | description |
|---|---|
| initialDelaySeconds | 容器启动后,探测开始之前的时间(单位为:s) |
| periodSeconds | 探测频率,默认值为:10s. 最小值为 1s |
| timeoutSeconds | 探测请求发出后,等待响应的时间(单位为:s),超时会触发重启容器。默认值为:1s ,最小值为:1s |
| successThreshold | 探测失败后,再次判断容器健康的探测次数。默认值为:1 ,最小值为:1。 |
| failureThreshold | 容器启动后,探测失败,kubernetes 在重启容器前,尝试再次判断容器是否健康的次数,即失败重试。如果设置在 readiness 中,则 Service 对应的 EndPoint 列表中将不会存在 此 Pod 对应的 End Point。默认值为:3 ,最小值为 1。 |
不同类型探针的相关配置
ExecAction
只存在 command ,即只能以执行自定义命令的方式进行探测。
TCPSocketAction
只需要设置需要建立 TCP 连接的 port。
HTTPGetAction
| configure http probe | description |
|---|---|
| host | 主机名,默认为Pod IP |
| scheme | 请求方式 (HTTP 或者 HTTPS ), 默认值为: HTTP |
| path | 访问路径 |
| httpHeaders | 请求头 |
| port | 访问容器的端口号,范围 :[1,65535) |
Pod readiness gate
除了上述的两种方式,在 kubernetes 1.14 中 readiness gate 发布了 stable 版本。这个属性在 1.11 时加入,当时命令为 Pod ready++
例子:
Kind: Pod
...
spec:
readinessGates:
- conditionType: "www.example.com/feature-1"
status:
conditions:
- type: Ready # this is a builtin PodCondition
status: "False"
lastProbeTime: null
lastTransitionTime: 2018-01-01T00:00:00Z
- type: "www.example.com/feature-1" # an extra PodCondition
status: "False"
lastProbeTime: null
lastTransitionTime: 2018-01-01T00:00:00Z
containerStatuses:
- containerID: docker://abcd...
ready: true
...
根据官网的文档,我们可以在 spec 定义期望 readinessGates 来检测 Pod 是否健康,需要在 status.conditions 设置 type: "www.example.com/feature-1" 自定义一个 condition ,如果不设置,默认为 false , 并且这个condition 的 status 可以被外部修改,也就是说我们可以外部设置这个 Pod 是否能够被 Service 调度到。
设置了 readinessGates 之后判断一个 Pod 是否健康的条件
- Pod 中所有的容器都为 ready 状态
- 设置的所有的 ReadinessGates 状态都为 true
只有满足以上两个条件,这个 Pod 参可能被认为可暴露的,也就是说 Service 对应的 EndPoint 列表中才会包含这个 Pod 对应的 EndPoint。